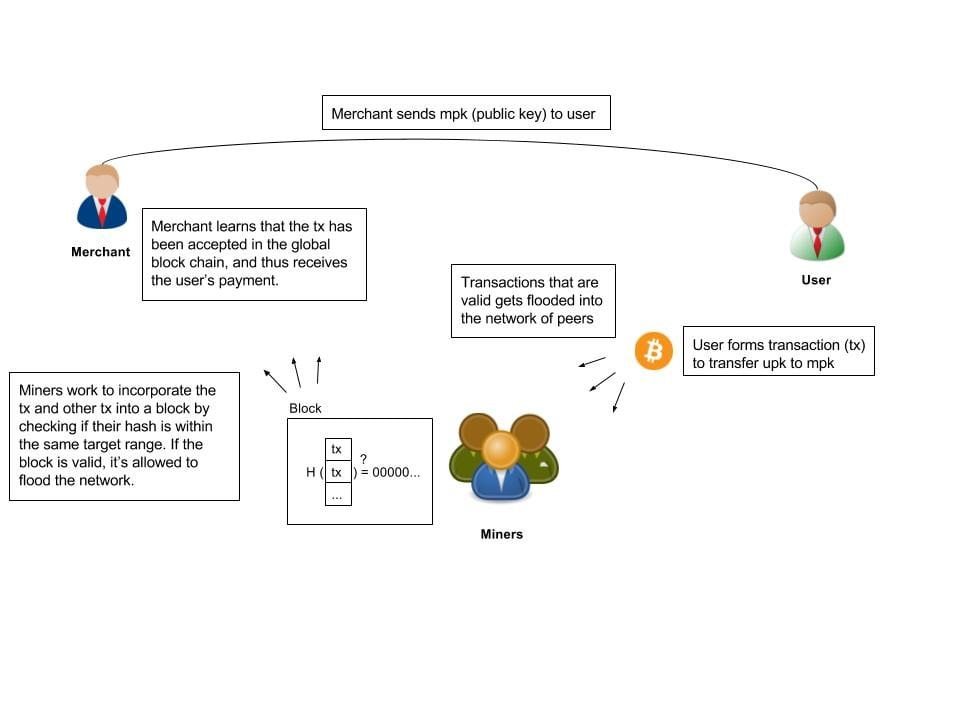
Transactions over the internet means that you’re not able to see, or at least verify the other person’s actions. Hence, a neutral third party that can oversee and verify both parties. In this case, it’s either the banks or payment gateways that act as agents to carry out transactions.
Blockchain technology eliminates the need for third party intervention. We know that the ecosystem is made up of a large network of computers. Furthermore, it continually grows as more people join the network. The idea of a peer-to-peer network is that instead of one intermediary, there is a large pool of validators that reaches a consensus to validate a transaction.
Think of it in terms of witnesses. One witness is insufficient to verify that a crime happened. But if there were a lot of witnesses at the location, you can be sure that a crime did happen. In this case, instead of eye witnesses, blockchain uses mathematical verification. Which is a whole lot more reassuring, if you ask me.
What is worth noting is that the larger the size of the network, the more secure it is. To date, bitcoin is secured 3,500,000 T/Hs, which simply means that you need a lot of computing power to crack the hash code. You can learn more about what hash means from our post here.